| Image | Title | Summary | Categories | Tags | hf:categories | hf:tags |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
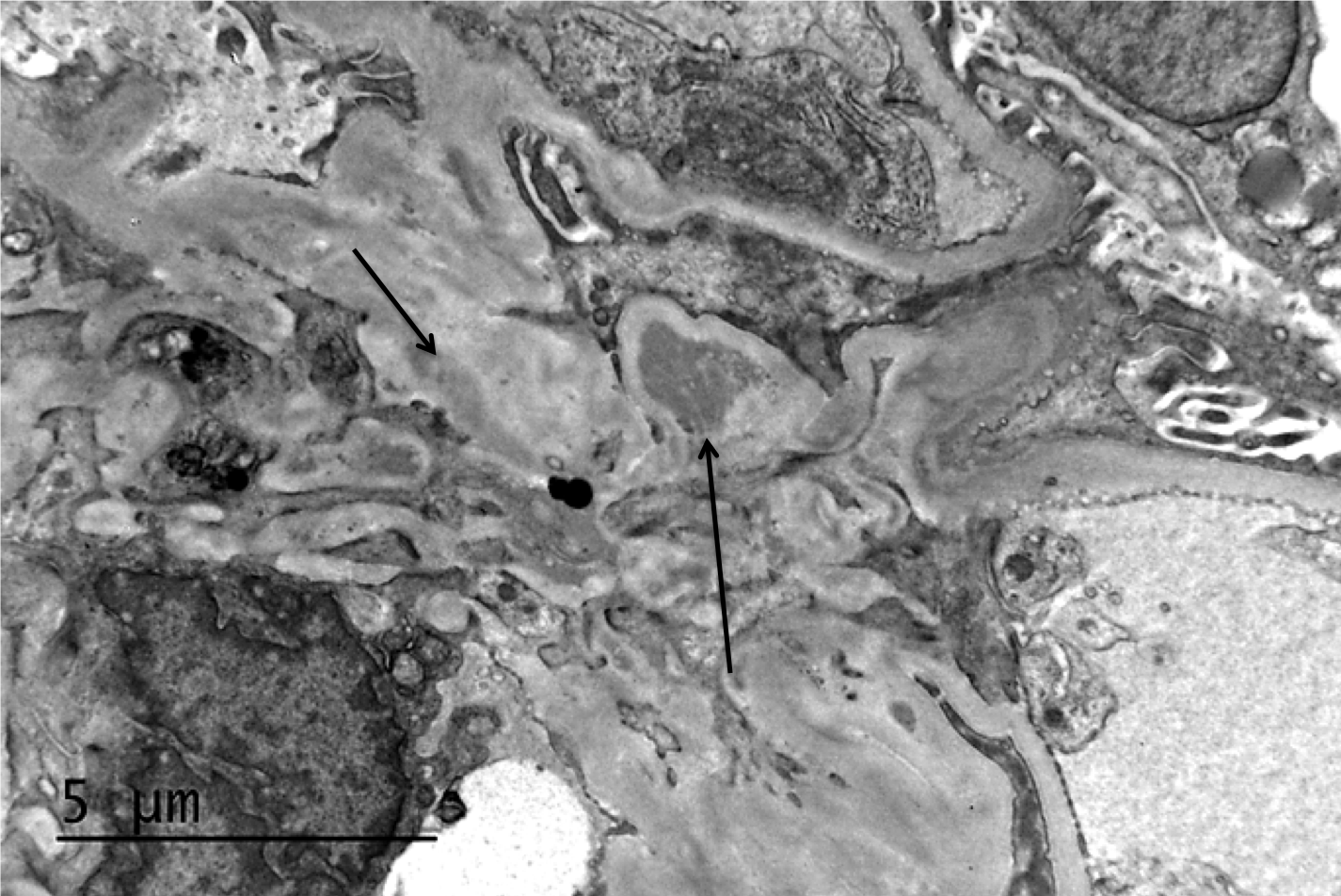
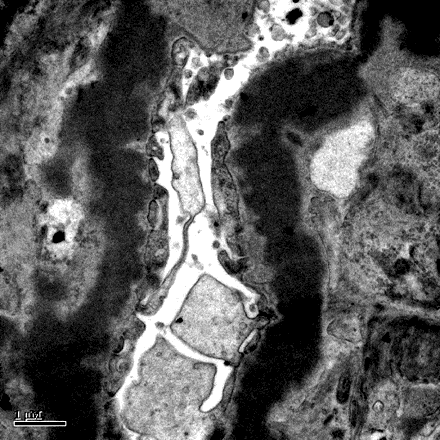
| Mesangial Deposits | Electron microscopy of a biopsy specimen in a patient with IgA nephropathy. Electron dense deposits can be identified in the mesangium (black arrows), which on immunofluorescence would have predominant or co-dominant IgA staining. Note that although mesangial IgA deposits are classic in IgA nephropathy and IgA vasculitis (former Henoch-Schonlein purpura nephritis), they can be seen in other conditions including infection-associated glomerulonephritis, inflammatory bowel disease, malignancies, sarcoidosis, and certain dermatologic conditions. GBM; glomerular basement membrane. RBC; red blood cells. Mes; mesangium. CS; capillary space. Images courtesy of Patrick Walker, … | General Renal Pathology, Glomerular Diseases | electron dense deposits, electron microscopy, IgA nephropathy, immunofluorescence, mesangium | general-renal-pathology glomerular-disease | electron-dense-deposits electron-microscopy iga-nephropathy immunofluorescence mesangium | |
| Perihilar FSGS | Perihilar variant of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS). Hyaline deposition and sclerosis occur at the vascular pole of the glomerulus. This variant is believed to be a secondary form of FSGS, occurring as an adaptive response to other injuries resulting in loss of functioning nephrons, such as in obesity-related kidney disease. Images courtesy of Patrick Walker, … | Glomerular Diseases | FSGS, light microscopy, obesity | glomerular-disease | fsgs light-microscopy obesity | |
| Glomerulomegaly | A normal glomerulus (left) and hypertrophied glomerulus (glomerulomegaly, right). Glomerulomegaly is an adaptive response to decreased nephron number (e.g. prematurity) and/or increased demand (e.g. obesity). Patients with glomerulomegaly may have sub-nephrotic or nephrotic-range proteinuria, but other features of nephrotic syndrome are rare. Images courtesy of Patrick Walker, … | General Renal Pathology, Glomerular Diseases | glomerulomegaly, light microscopy | general-renal-pathology glomerular-disease | glomerulomegaly light-microscopy | |
| Segmental glomerulosclerosis in IgA nephropathy | A patient with IgA nephropathy and associated segmental glomerulosclerosis. Images courtesy of Patrick Walker, … | Glomerular Diseases, Uncategorized | glomerulosclerosis, IgA nephropathy, immunofluorescence, light microscopy | glomerular-disease uncategorized | glomerulosclerosis iga-nephropathy immunofluorescence light-microscopy | |
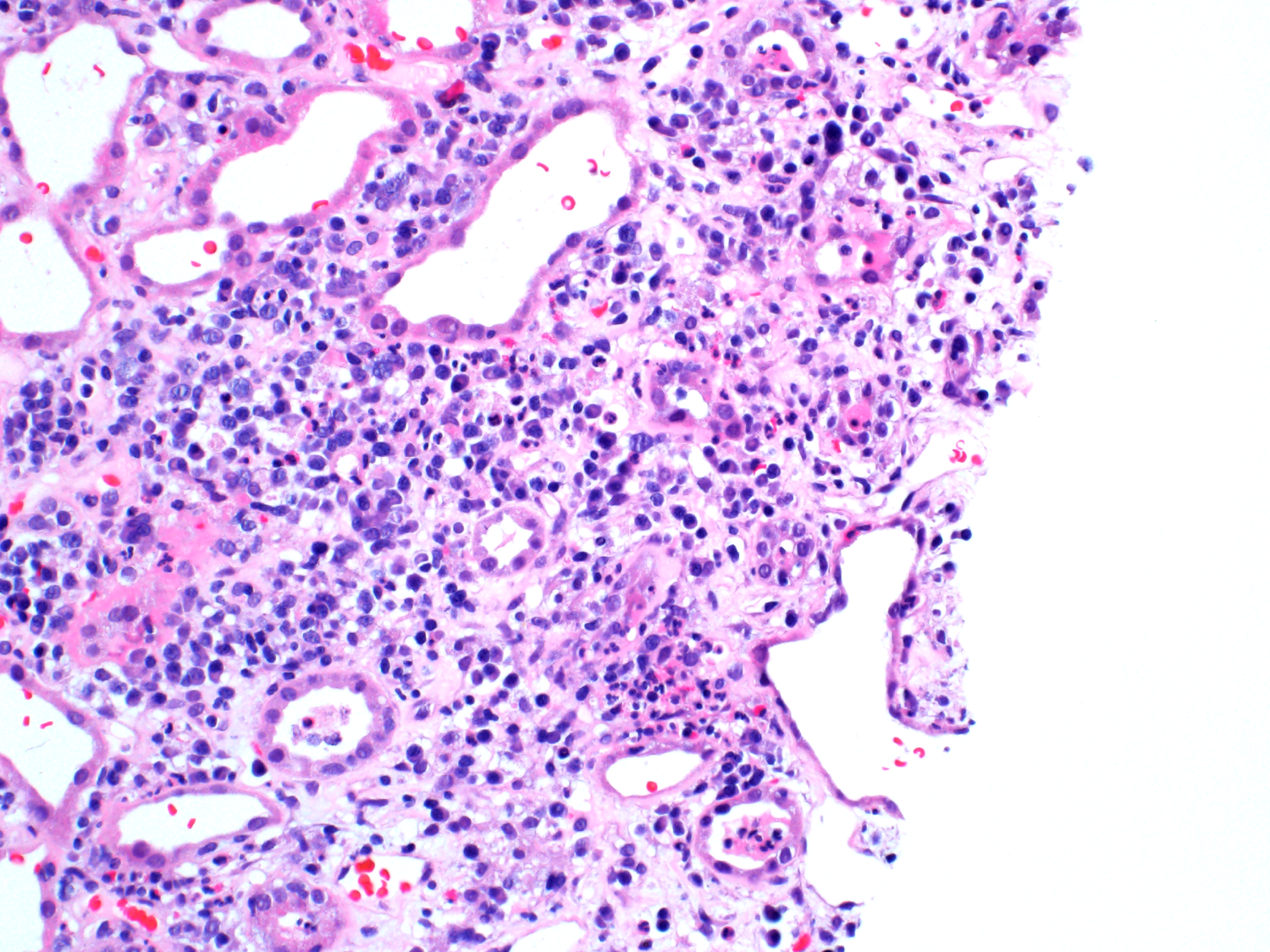
| Acute interstitial nephritis | A mixed inflammatory cell infiltrate in a child with acute interstitial nephritis. Image courtesy of Patrick Walker, … | Tubular Diseases | acute interstitial nephritis, light microscopy | tubulointerstitial-disease | acute-interstitial-nephritis light-microscopy | |
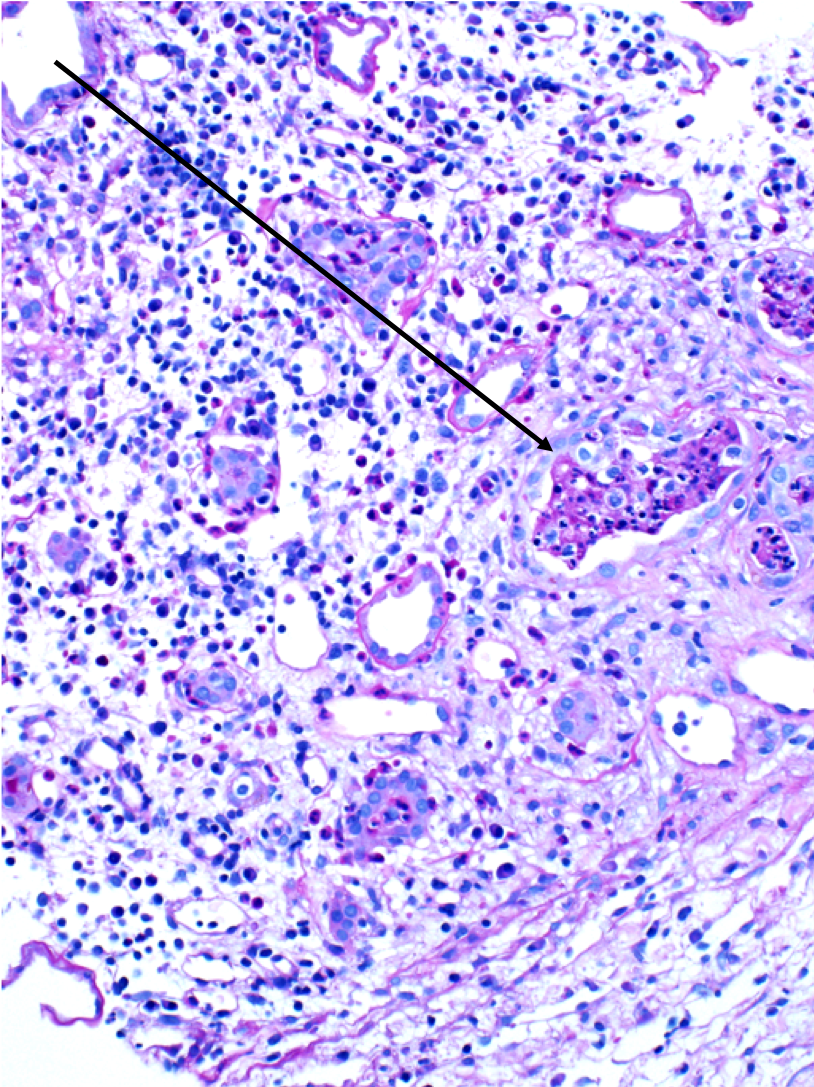
| WBC casts | WBC casts (black arrows) in a biopsy specimen of a patient with acute interstitial nephritis. Images courtesy of Patrick Walker, … | General Renal Pathology, Tubular Diseases | acute interstitial nephritis, light microscopy, WBC casts | general-renal-pathology tubulointerstitial-disease | acute-interstitial-nephritis light-microscopy wbc-casts | |
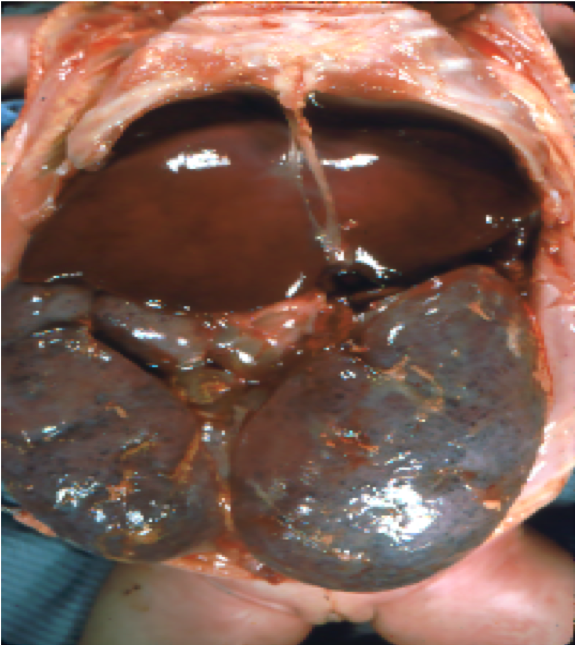
| Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD) | Gross pathology and low-power light microscopy of kidney tissue in a neonate with ARPKD. The kidneys are enlarged but maintain their reniform shape, and are full of microscopic cysts derived from dilated distal tubules and cortical collecting ducts. Images courtesy of Patrick Walker, MD. … | Genetic Diseases, Tubular Diseases | gross pathology, light microscopy, polycystic kidney disease, renal cysts | genetic-diseases tubulointerstitial-disease | gross-pathology light-microscopy polycystic-kidney-disease renal-cysts | |
| Simple renal cysts | Microscopic renal cysts. Note the flattened to cuboidal epithelium lining the cysts. Images courtesy of Patrick Walker, … | General Renal Pathology, Tubular Diseases | light microscopy, renal cysts | general-renal-pathology tubulointerstitial-disease | light-microscopy renal-cysts | |
| Crescents | A segmental (left, black arrow) and circumferential crescent (right) in a patient with IgA nephropathy. Images courtesy of Patrick Walker, … | General Renal Pathology, Glomerular Diseases | crescentic glomerulonephritis, IgA nephropathy, light microscopy | general-renal-pathology glomerular-disease | crescentic-glomerulonephritis iga-nephropathy light-microscopy | |
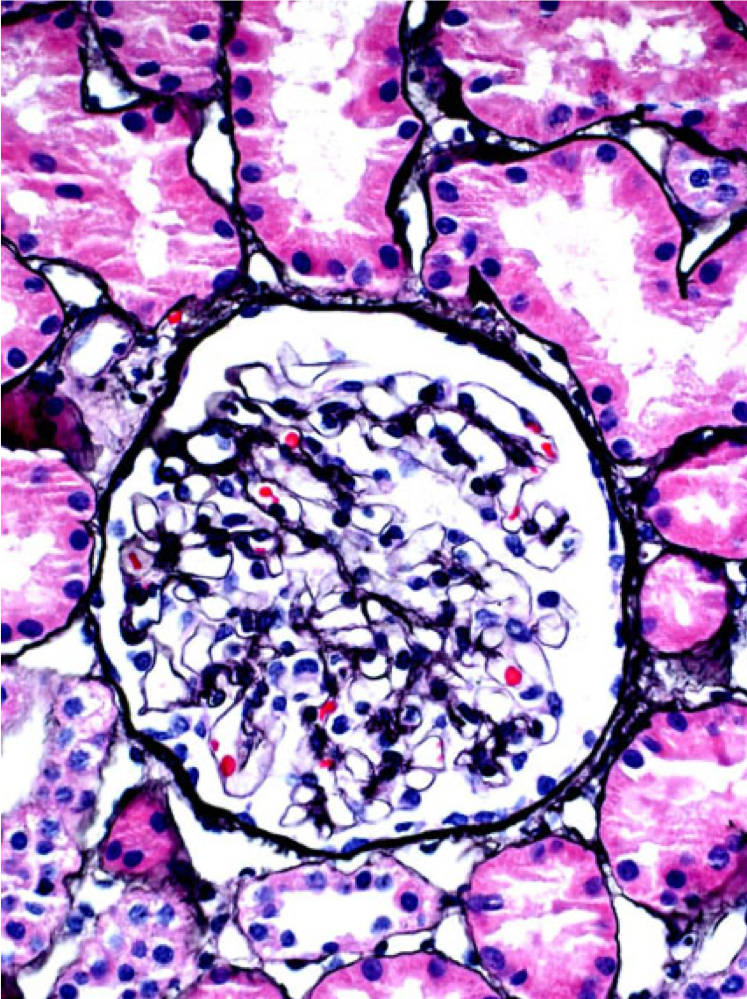
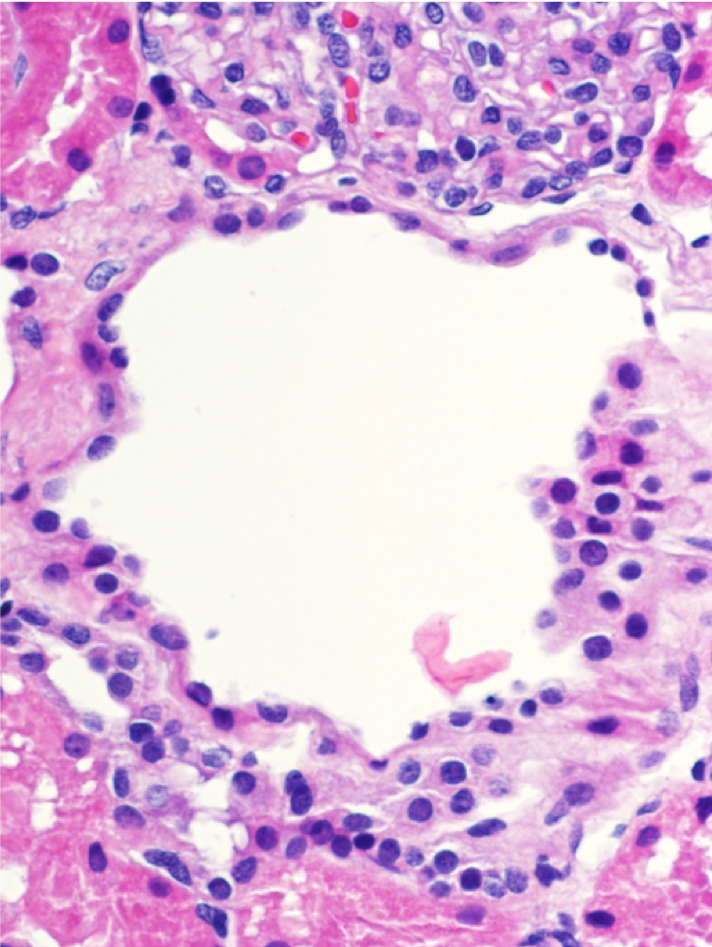
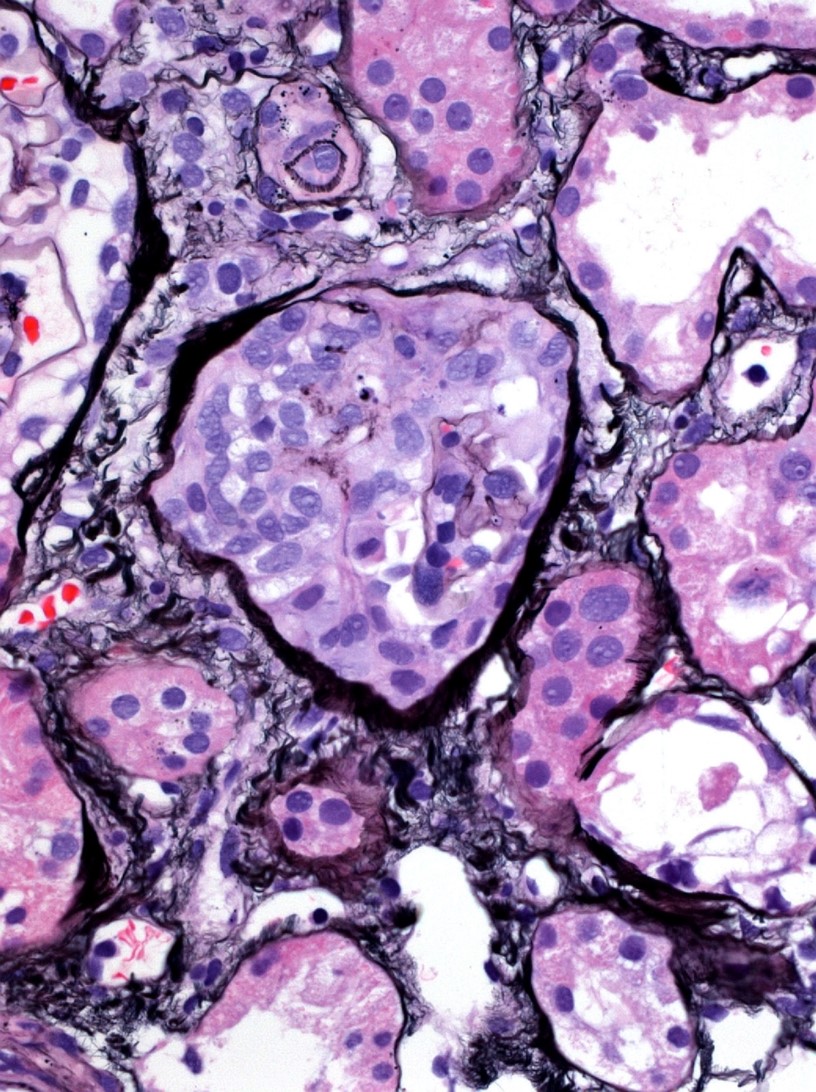
| Endocapillary hypercellularity | A normal appearing glomerulus (left) compared to a glomerulus with endocapillary hypercellularity (right). Note the hypercellular capillary loop (red arrow) compared to the normal capillary lumens (black arrows). This histologic feature can be seen in several glomerular disorders, including IgA nephropathy, post-infectious glomerulonephritis, lupus nephritis, and C3 glomerulopathy. Images courtesy of Patrick Walker, … | General Renal Pathology, Glomerular Diseases | IgA nephropathy, light microscopy, lupus nephritis, MPGN/C3 glomerulopathy, Post infectious glomerulonephritis | general-renal-pathology glomerular-disease | iga-nephropathy light-microscopy lupus-nephritis mpgn-c3-glomerulopathy post-infectious-glomerulonephritis | |
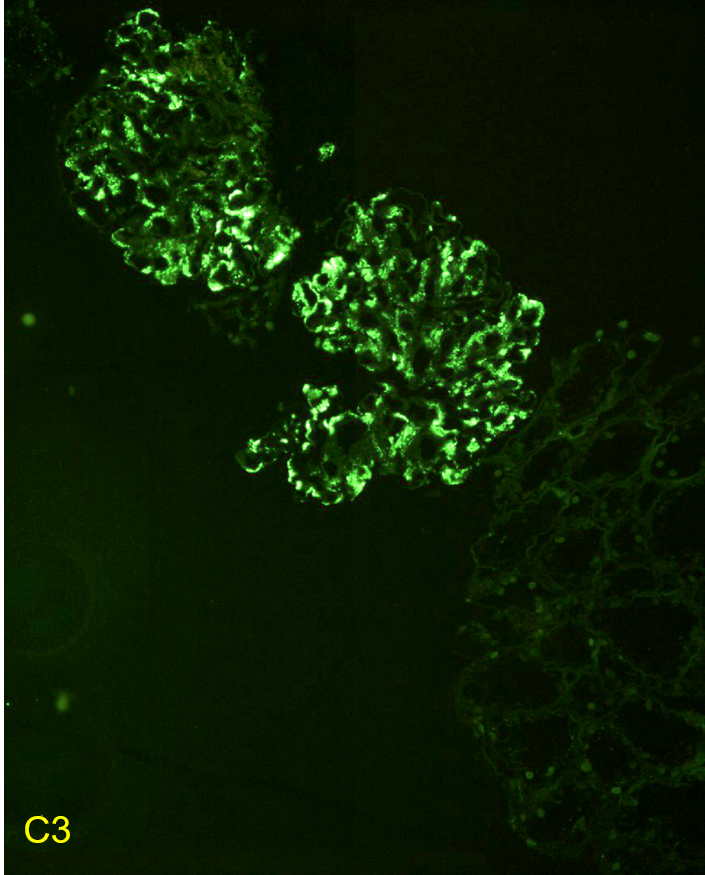
| Immunofluorescent staining in C3 glomerulopathy | Immunofluorescent staining pattern in a patient with C3 glomerulopathy. There is strong C3 staining in the capillary loops and mesangium. Immunoglobulin staining, such as IgG, is typically absent or at a lower intensity by at least two orders of magnitude than C3. Images courtesy of Patrick Walker, … | Glomerular Diseases | immunofluorescence, MPGN/C3 glomerulopathy | glomerular-disease | immunofluorescence mpgn-c3-glomerulopathy | |
| Dense deposit disease | Dense deposit disease on electron microscopy in a patient with C3 glomerulopathy. This lesion results from intramembranous transformation of the glomerular basement membrane by sausage-like, “osmiophilic” dense material. Images courtesy of Patrick Walker, … | Glomerular Diseases | Dense deposit disease, electron microscopy, MPGN/C3 glomerulopathy | glomerular-disease | dense-deposit-disease electron-microscopy mpgn-c3-glomerulopathy | |
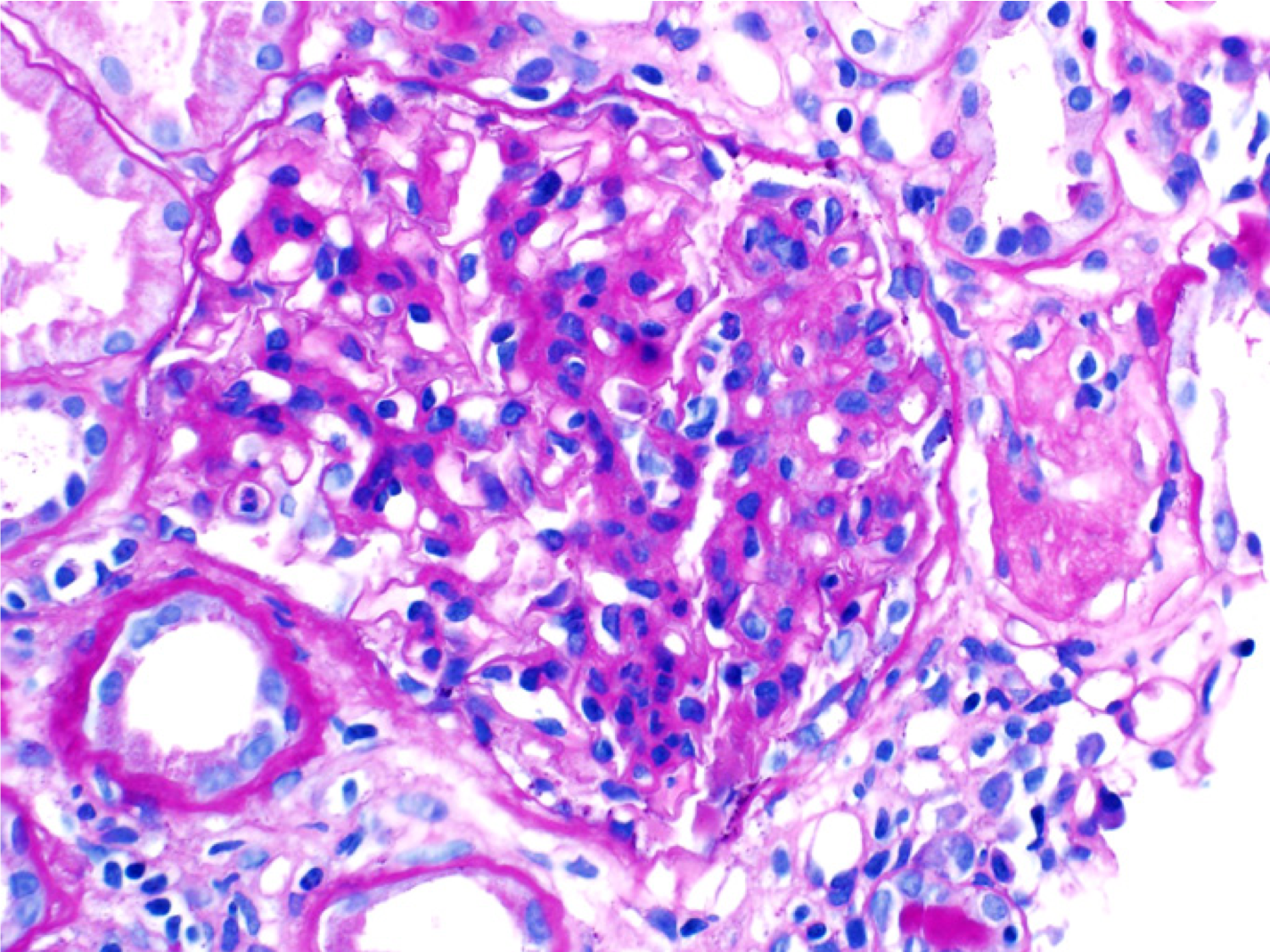
| Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis | Membranoproliferative pattern of glomerular injury in a patient with C3 glomerulopathy. This pattern of injury typically has endocapillary proliferation, diffuse capillary wall thickening, increased mesangial matrix, and mesangial proliferation visible on light microscopy, producing a lobular appearance of the glomerular tuft. Images courtesy of Patrick Walker, … | Glomerular Diseases | light microscopy, MPGN/C3 glomerulopathy | glomerular-disease | light-microscopy mpgn-c3-glomerulopathy | |
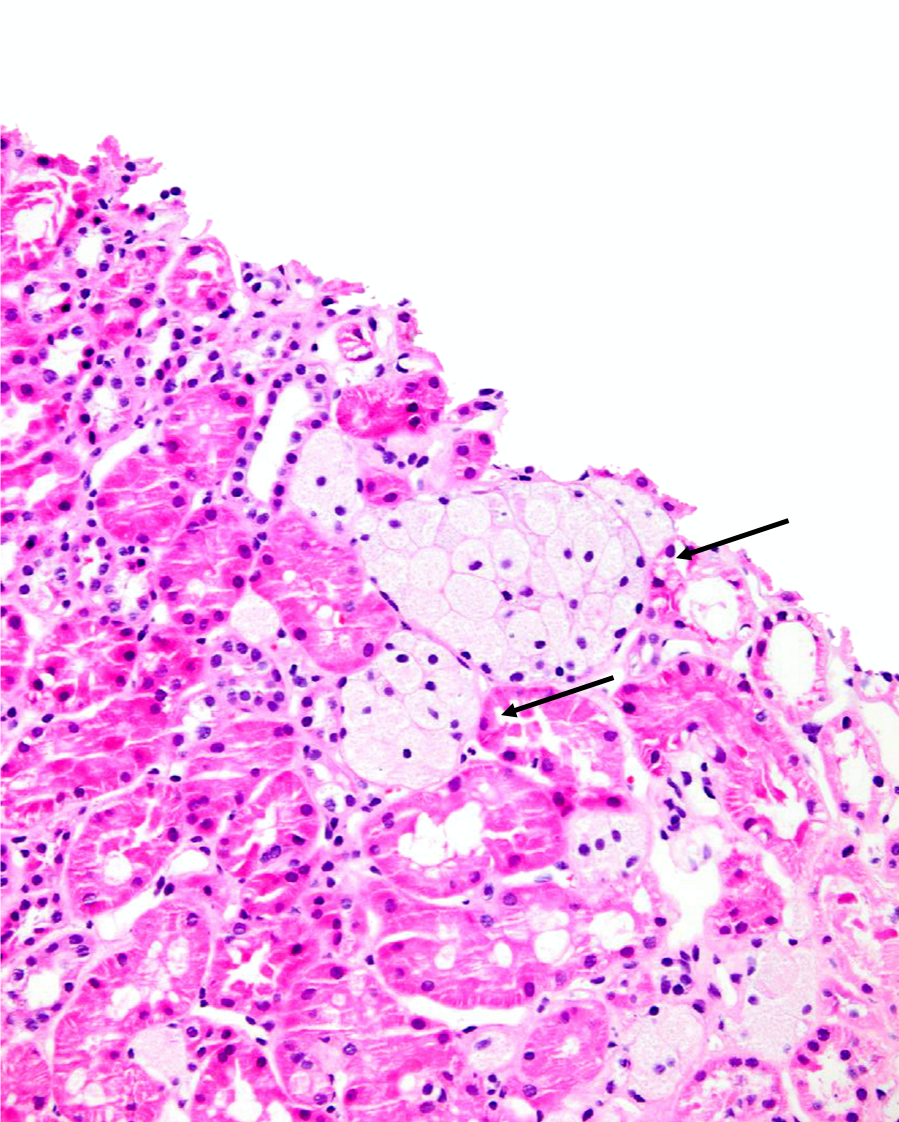
| Foam Cells | Clusters of interstitial foam cells (arrows) in a kidney biopsy. These are commonly found in biopsy specimens of patients with Alport syndrome, FSGS, IgA nephropathy, and other proteinuric kidney diseases. Image courtesy of Patrick Walker, … | General Renal Pathology | foam cells, light microscopy, proteinuria | general-renal-pathology | foam-cells light-microscopy proteinuria | |
| Acute interstitial nephritis | Acute interstitial nephritis with associated acute tubular injury. There is interstitial edema and the tubules are not back to back as would be expected, due to the inflammatory and lymphocytic infiltrate in the interstitial compartment. Note the interstitial eosinophils present in the second image (black arrows). Images courtesy of Joseph Gaut, MD … | Tubular Diseases | acute interstitial nephritis, light microscopy | tubulointerstitial-disease | acute-interstitial-nephritis light-microscopy | |
| Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis | Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) in a child presenting with nephrotic syndrome. Image courtesy of Joseph Gaut, MD … | Glomerular Diseases | FSGS, light microscopy, nephrotic syndrome | glomerular-disease | fsgs light-microscopy nephrotic-syndrome | |
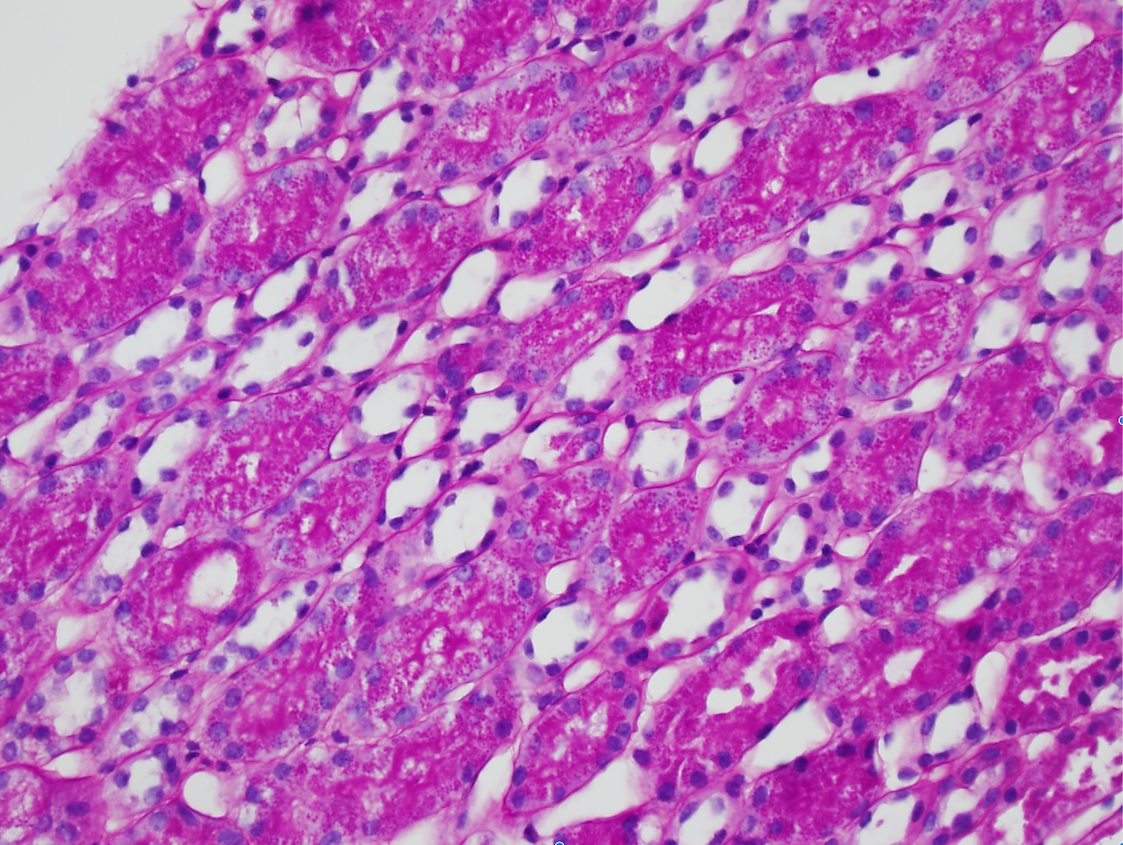
| Minimal change disease | Numerous PAS-positive protein reabsorption droplets in the renal tubules of a child with minimal change disease. Image courtesy of Joseph Gaut, MD … | Glomerular Diseases | light microscopy, minimal change disease, nephrotic syndrome | glomerular-disease | light-microscopy minimal-change-disease nephrotic-syndrome | |
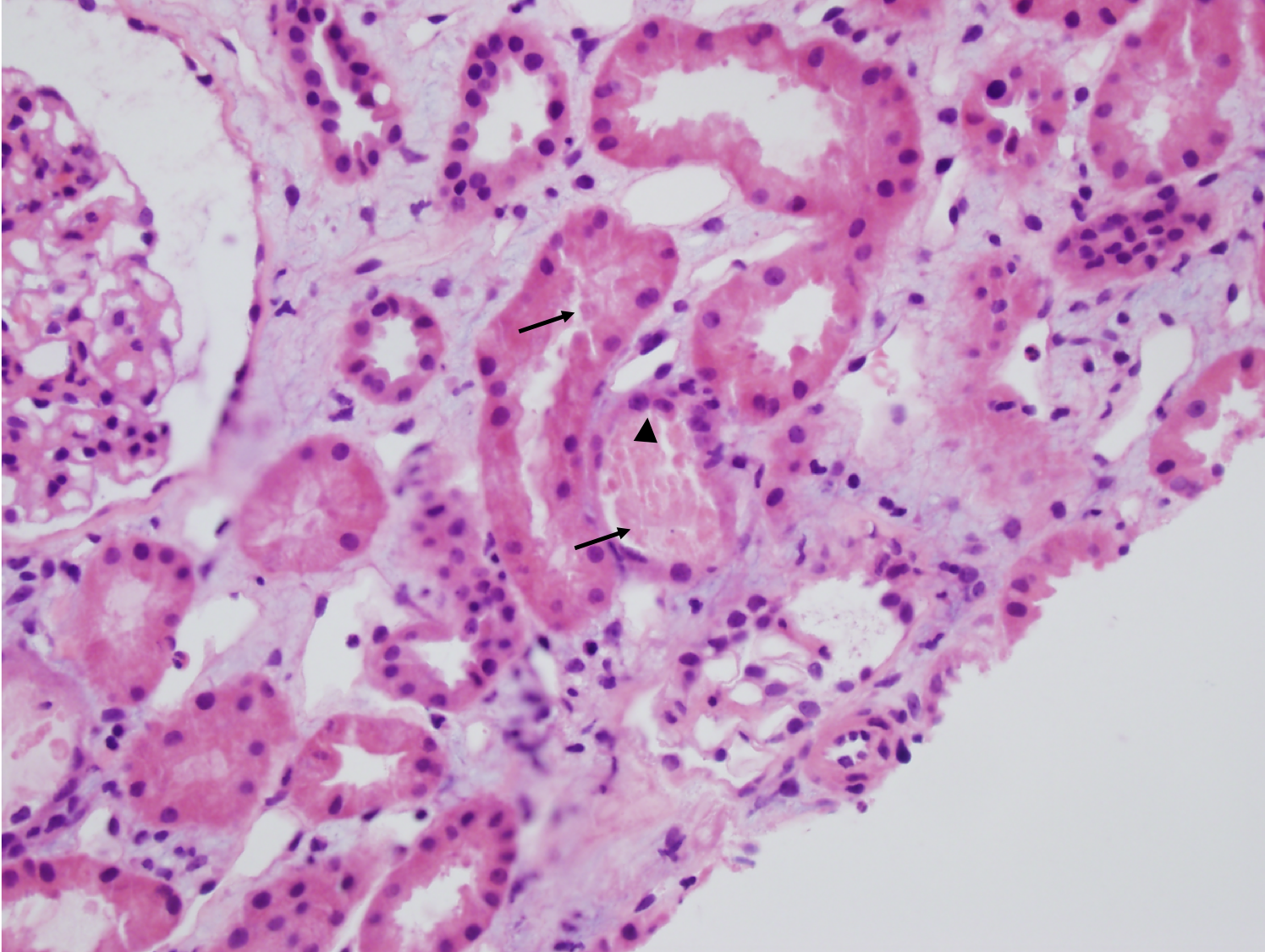
| Acute tubular necrosis | Acute tubular necrosis (ATN). Note the tubules are not back-to-back due to interstitial edema (Masson trichrome staining, not shown, did not show appreciable fibrosis). There is blebbing and sloughing of tubular epithelial cells (black arrows) with loss of the brush border, as well as flattening of the renal tubular epithelium (black arrowhead) due to tubular dilation. Image courtesy of Joseph Gaut, MD … | Tubular Diseases | acute kidney injury, acute tubular necrosis, light microscopy | tubulointerstitial-disease | acute-kidney-injury acute-tubular-necrosis light-microscopy | |
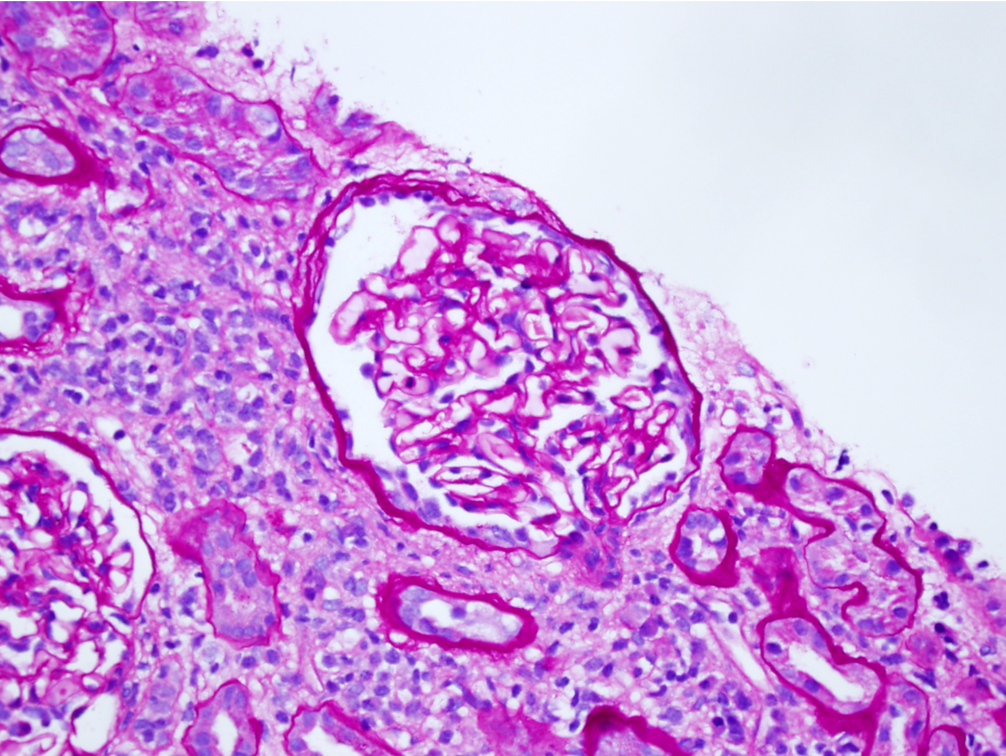
| IgA nephropathy | IgA nephropathy with crescents. Note the fibrocellular crescent present in this glomerulus extending from the 3 o’clock the 12 o’clock position. Though difficult to appreciate in this image, there is mild mesangial hypercellularity. Image courtesy of Joseph Gaut, MD … | Glomerular Diseases | crescentic glomerulonephritis, IgA nephropathy | glomerular-disease | crescentic-glomerulonephritis iga-nephropathy | |
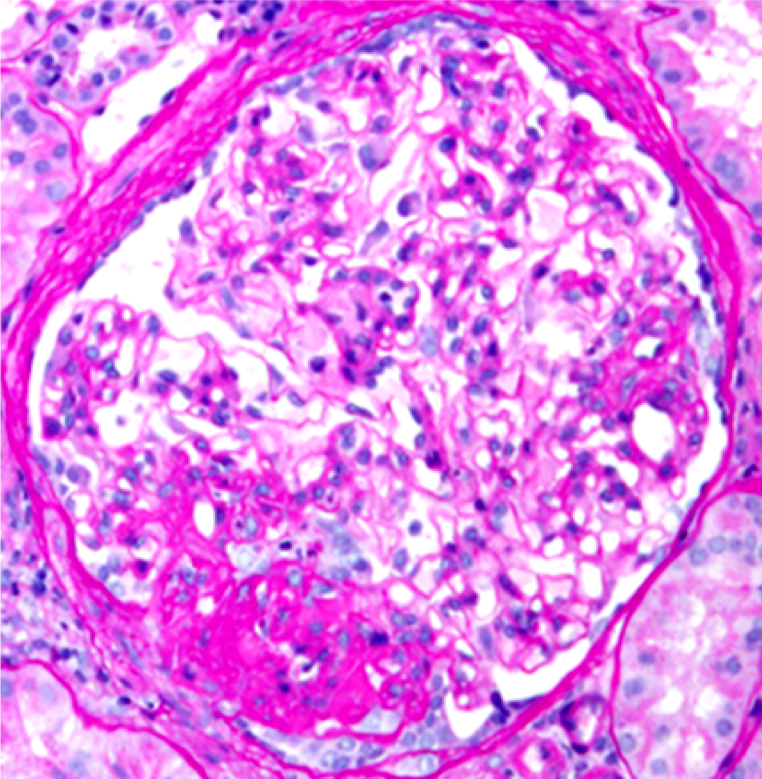
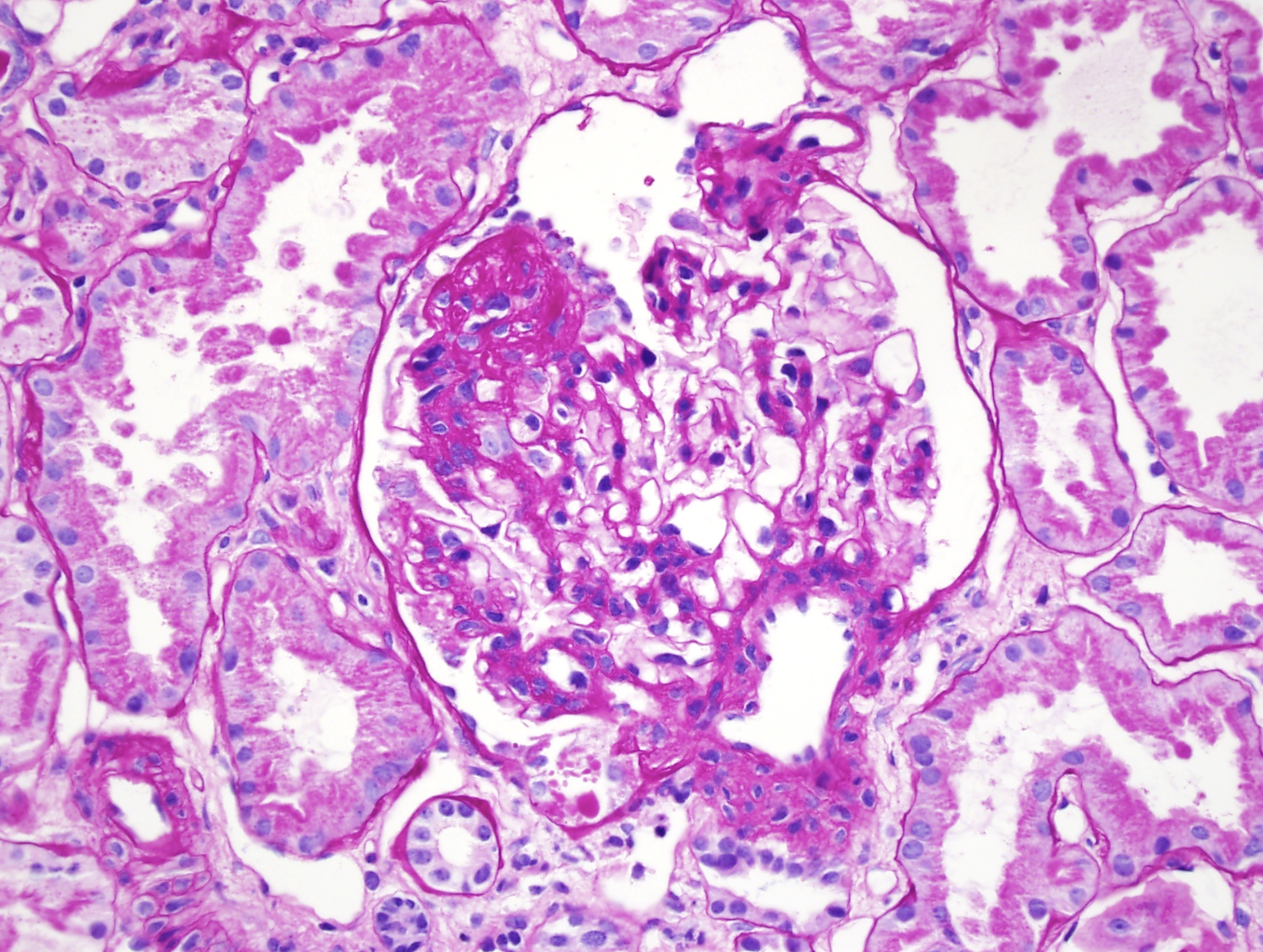
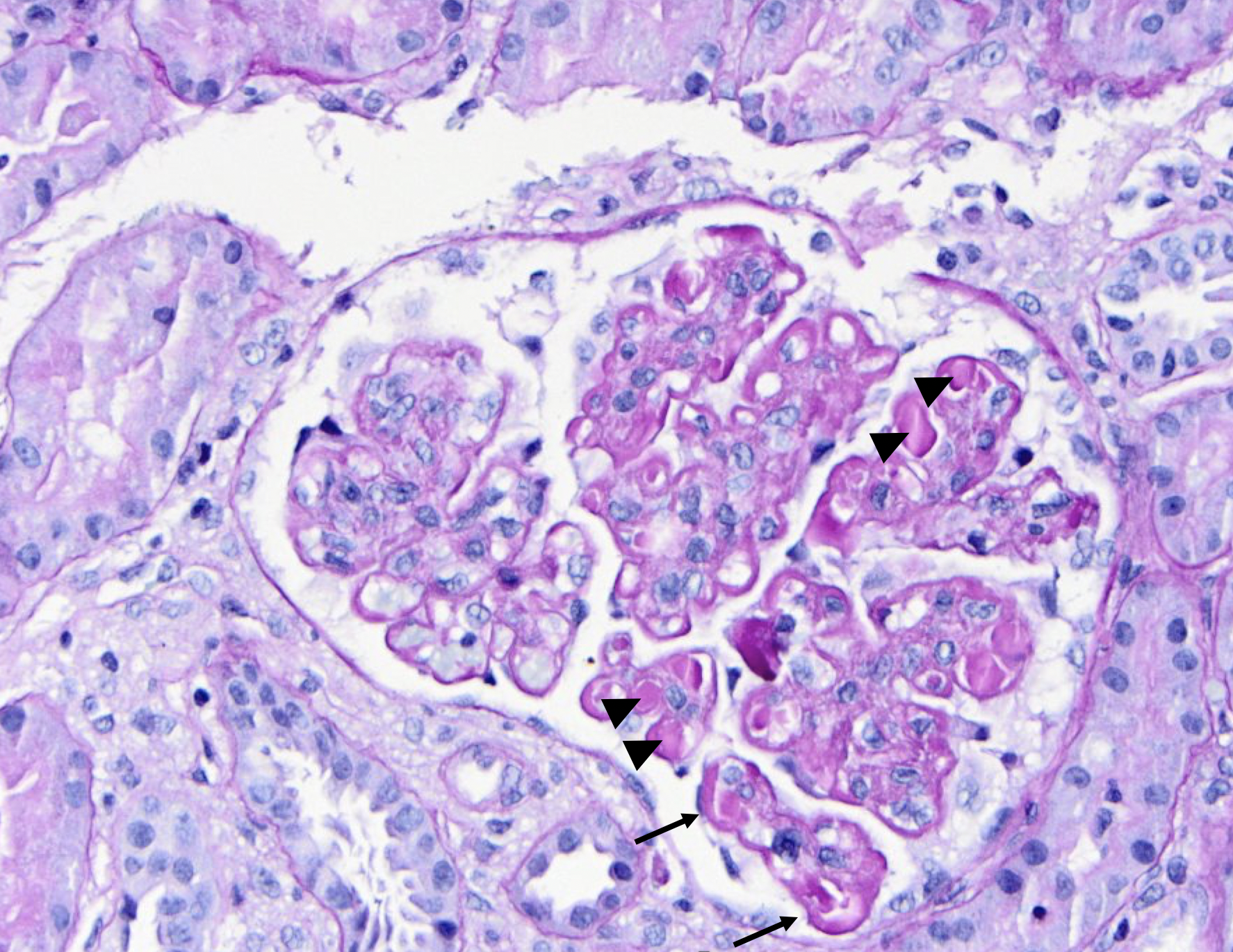
| SLE nephritis | PAS stain of a glomerulus in a patient with SLE nephritis. There is endocapillary and mesangial proliferation, as evidenced by thickened, occlusive capillary loops and increased mesangial cellularity. Note the “wire loop” lesions (arrows) and hyaline thrombi present (arrowheads). Image courtesy of Joseph Gaut, MD, … | Glomerular Diseases | light microscopy, SLE nephritis | glomerular-disease | light-microscopy sle-nephritis | |
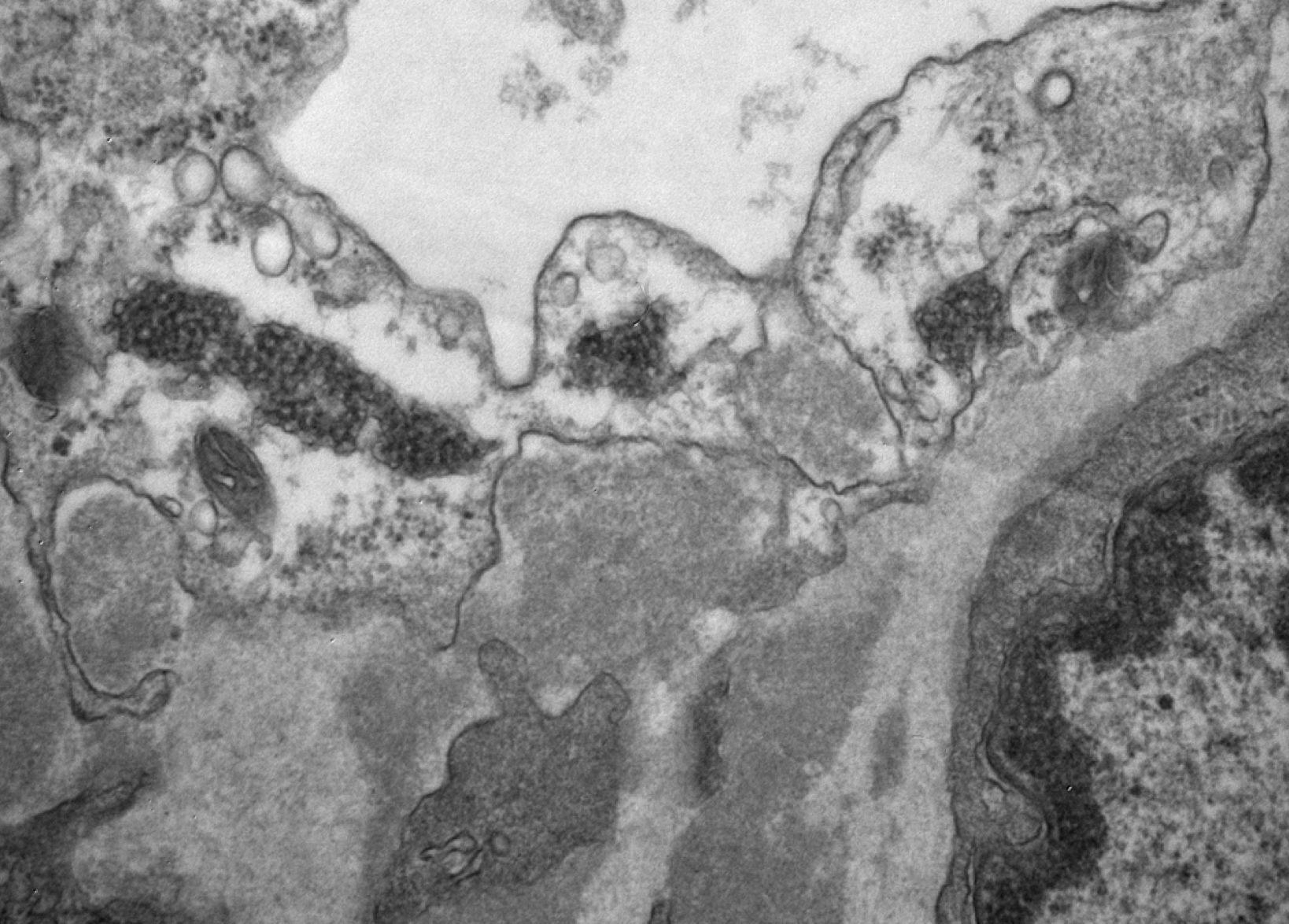
| Tubuloreticular inclusions in SLE nephritis | Tubuloreticular inclusions in a patient with diffuse proliferative SLE nephritis (SLE class IV). These subcellular structures (dark circular clusters) on transmission electron microscopy are localized to the cytoplasm of endothelial cells, and thought to be formed in high interferon states. These are classic for SLE nephritis, but can be seen in other glomerular conditions as well including membranous nephropathy, ANCA-associated vasculitis, and infection-associated glomerulonephritis. Image courtesy of Joseph Gaut, MD, … | Glomerular Diseases | electron microscopy, SLE nephritis, tubuloreticular inclusions | glomerular-disease | electron-microscopy sle-nephritis tubuloreticular-inclusions | |
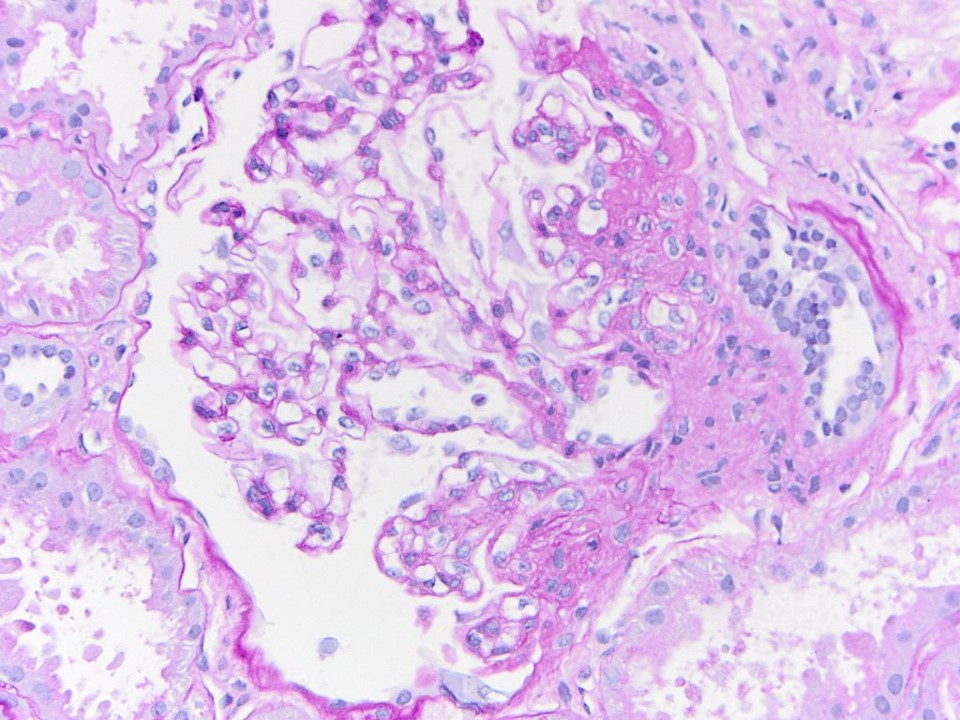
| Focal and segmental glomerulosclerosis | Segmental obliteration of the glomerular capillary lumen in a patient with FSGS. Note the sclerotic portion of the glomerular tuft is adherent to Bowman’s capsule. There is proximal tubular hypertrophy, which can be seen in this condition in response to heavy proteinuria. Image courtesy of Brian Stotter, … | Glomerular Diseases | FSGS, light microscopy | glomerular-disease | fsgs light-microscopy |